Paxata vs Trifacta
Author: Michael Stromann
1
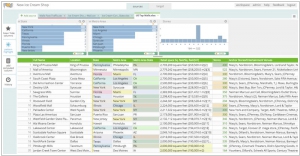
Paxata is a self-service data preparation solution designed to help everyone who deals with data eliminate the pain of combining, cleaning and shaping their data prior to analytics. Business analysts work within an Excel-like application that is easy to use, with visually interactive guidance that makes it easy to bring together data, find and fix dirty or missing data, and share and re-use data projects across teams. IT organizations and curators leverage the Paxata platform as a shared environment for delivering data, monitoring how data is prepared and used, and building dynamic governance that is aligned with the semantics of the business, not data systems.
9
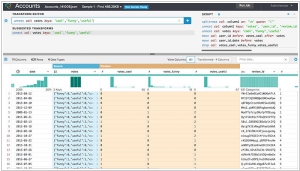
Trifacta's Data Transformation Platform increases productivity up to 10x. Trifacta’s Data Profiling features provide immediate visibility into unique elements of the data set like data distributions and outliers to inform the transformation and analysis process. Trifacta’s automated detection of data types, value distribution and missing or inconsistent values provides the user with immediate cues to a dataset’s fit and trustworthiness.
See also:
Top 10 Big Data platforms
Top 10 Big Data platforms
Paxata and Trifacta are both data preparation platforms that are used for cleaning, transforming, and enriching raw data for analysis and insights. However, there are some key differences between these two platforms:
User Interface and Ease of Use: Paxata and Trifacta have different user interfaces and approaches to data preparation. Paxata focuses on a visual, spreadsheet-like interface where users can interact with data using a grid-based view, making it easy for business users to manipulate data without requiring extensive technical skills. Trifacta, on the other hand, uses a visual interface that allows users to create data preparation workflows using a combination of visual representations and code-based transformations. Trifacta is known for its advanced data wrangling capabilities and provides more flexibility and power for users who are comfortable with coding and data manipulation.
Automation and Intelligence: Both Paxata and Trifacta offer various automated data preparation features, such as data profiling, data cleansing, and data enrichment. However, Trifacta has a stronger focus on machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities for data preparation. Trifacta uses machine learning algorithms to suggest transformations and provide recommendations to users based on their data and usage patterns, making it easier to automate and streamline the data preparation process.
Connectivity and Integration: Paxata and Trifacta have different levels of connectivity and integration with other data sources and platforms. Paxata provides connectivity to a wide range of data sources, including databases, spreadsheets, cloud storage, and more, and allows users to import and export data in various formats. Trifacta also supports connectivity to various data sources, but it has a stronger integration with big data platforms such as Hadoop and Spark, making it suitable for large-scale data preparation and processing in big data environments.
Deployment Options: Paxata and Trifacta offer different deployment options to suit different needs and preferences. Paxata offers both cloud-based and on-premises deployment options, allowing users to choose between a cloud-based SaaS solution or an on-premises installation behind their own firewall. Trifacta, on the other hand, is primarily offered as a cloud-based SaaS solution, although it also provides a version that can be deployed on virtual private clouds (VPC) for customers who require more control over their data.
Pricing and Licensing: Pricing and licensing models may differ between Paxata and Trifacta, and it's important to review the details of their pricing and licensing offerings to determine which one aligns with your budget and requirements.
In summary, the main differences between Paxata and Trifacta include their user interface and ease of use, automation and intelligence capabilities, connectivity and integration options, deployment options, and pricing and licensing models.
See also: Top 10 Big Data platforms
User Interface and Ease of Use: Paxata and Trifacta have different user interfaces and approaches to data preparation. Paxata focuses on a visual, spreadsheet-like interface where users can interact with data using a grid-based view, making it easy for business users to manipulate data without requiring extensive technical skills. Trifacta, on the other hand, uses a visual interface that allows users to create data preparation workflows using a combination of visual representations and code-based transformations. Trifacta is known for its advanced data wrangling capabilities and provides more flexibility and power for users who are comfortable with coding and data manipulation.
Automation and Intelligence: Both Paxata and Trifacta offer various automated data preparation features, such as data profiling, data cleansing, and data enrichment. However, Trifacta has a stronger focus on machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities for data preparation. Trifacta uses machine learning algorithms to suggest transformations and provide recommendations to users based on their data and usage patterns, making it easier to automate and streamline the data preparation process.
Connectivity and Integration: Paxata and Trifacta have different levels of connectivity and integration with other data sources and platforms. Paxata provides connectivity to a wide range of data sources, including databases, spreadsheets, cloud storage, and more, and allows users to import and export data in various formats. Trifacta also supports connectivity to various data sources, but it has a stronger integration with big data platforms such as Hadoop and Spark, making it suitable for large-scale data preparation and processing in big data environments.
Deployment Options: Paxata and Trifacta offer different deployment options to suit different needs and preferences. Paxata offers both cloud-based and on-premises deployment options, allowing users to choose between a cloud-based SaaS solution or an on-premises installation behind their own firewall. Trifacta, on the other hand, is primarily offered as a cloud-based SaaS solution, although it also provides a version that can be deployed on virtual private clouds (VPC) for customers who require more control over their data.
Pricing and Licensing: Pricing and licensing models may differ between Paxata and Trifacta, and it's important to review the details of their pricing and licensing offerings to determine which one aligns with your budget and requirements.
In summary, the main differences between Paxata and Trifacta include their user interface and ease of use, automation and intelligence capabilities, connectivity and integration options, deployment options, and pricing and licensing models.
See also: Top 10 Big Data platforms